Understanding Data as a Service (DaaS)

Seema Karwa
Head of Sales
"We are generating 140 data elements per second across the two-wheeler segment where our battery is being used. How can we monetize this data?" This is what one of the clients mentioned in a discussion, which further led us to brainstorm the concept of 'Data as a Service' (DaaS). Until now, people have mostly heard about Software as a Service (SaaS). If we compare DaaS to SaaS, it works in a similar manner. Just as SaaS eliminates the need for software installation on devices and provides users with access to digital solutions over the network, DaaS also transfers most storage, integration, and processing operations to the cloud.
DaaS is essentially a data management strategy that utilizes the cloud to provide storage, integration, processing, and/or analytics services over a network connection. Data as a Service manages the stream of information and makes it accessible to all departments, anytime and anywhere. DaaS providers, like other "as a service" offerings, deliver data-centric insights through the cloud in a safe and cost-effective manner.
So, how does DaaS differ from Data as a Product (DaaP)?
During my research, I came across a post by Justin Gage (@itunpredictable) on Medium that explains the difference between DaaS and DaaP in the most simplistic fashion:
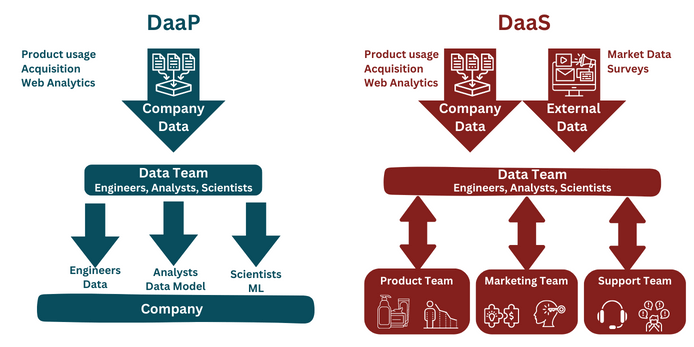
In the DaaP model, the company's data is treated as a product, and the flow of data is unidirectional, from the data team to the company. In the Data as a Product model, the data team's role is to deliver the data that the company requires for various purposes, such as making decisions, creating personalized products, or identifying fraud. It's as simple as that.
In a DaaS model, the focus of the data team is on answering questions rather than providing tools for others to solve their own issues. The data team collaborates with stakeholder groups to address specific problems using data under the Data as a Service model.
When should a business consider DaaS?
The data market is continuously expanding, with new methods of obtaining data in various forms through growing connectivity tools such as mobile phones, IoT sensors, and more. These technologies provide new types of data and innovative methods for analysis. Some applications where DaaS can come in handy include:
-
Analyzing company growth: With DaaS, you have access to global external data, including market and competitor's data. You can compare your company's performance with market trends and see how competitors are faring in similar market conditions.
-
Monetizing big data: As the volume of big data increases, one of the biggest challenges for companies is turning this vast amount of data into actual revenue. Bringing data into your company is just the beginning; you need a plan to utilize the data acquired from your consumers to generate better brand experiences and achieve a return on the investment made in these robust systems.
-
Building a data marketplace: Users can buy and sell data on these platforms, bringing various types of data together, including demographic data from business intelligence platforms and consumer data from customer relationship management (CRM) systems. For data scientists, the ability to instantly buy and sell data is a valuable asset.
-
Improving customer experience: DaaS can assist businesses in creating personalized customer experiences by utilizing predictive analytics to better understand customers, identify trends, serve them better, and increase loyalty.
Final Remarks:
DaaS is well-positioned to deliver the features that today's data-driven businesses desire, demand, or even require without their awareness. Despite being a relatively new solution, getting started with DaaS is easier than you may think. Please reach out to us for a deeper conversation about this topic.